Storyboard: Ocean Acidification in the Southern Ocean
Ocean acidification
Impact on marine ecosystems
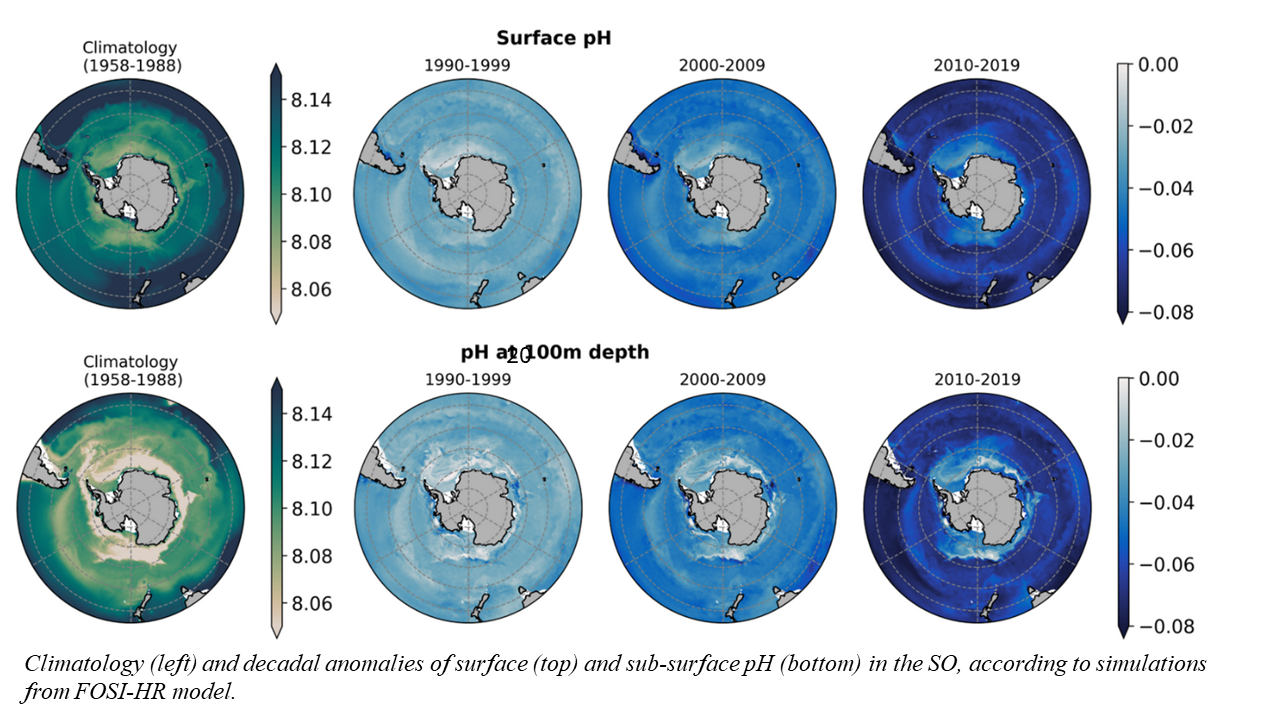
OA in the SO
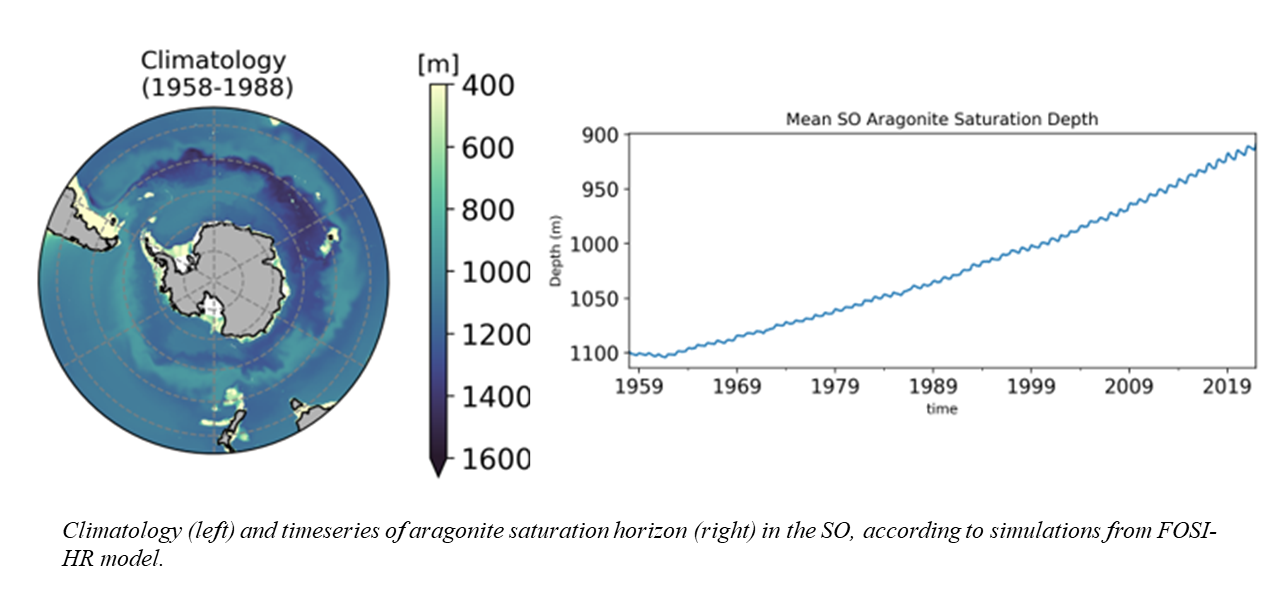
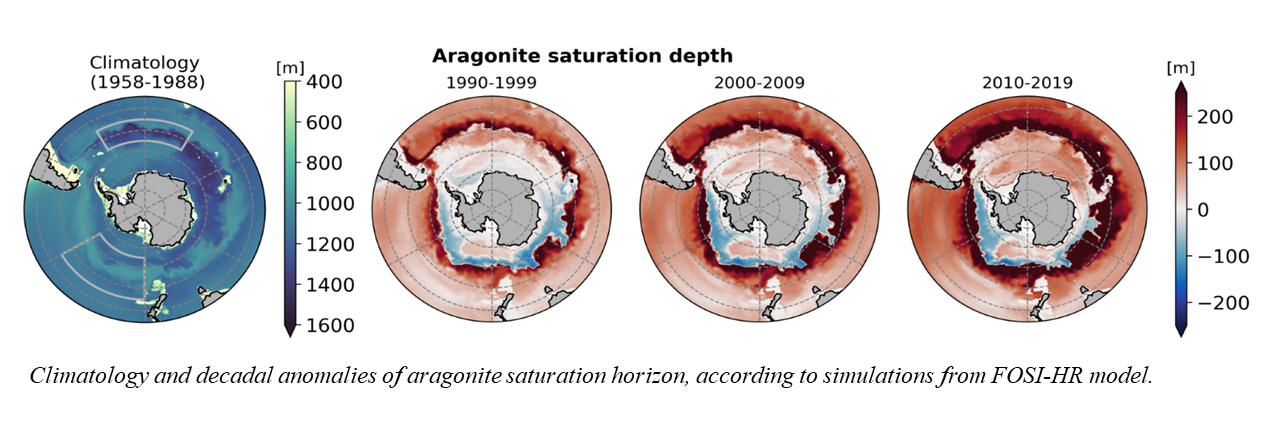
Aragonite saturation
Physics & aragonite saturation
The ocean: a critical carbon sink
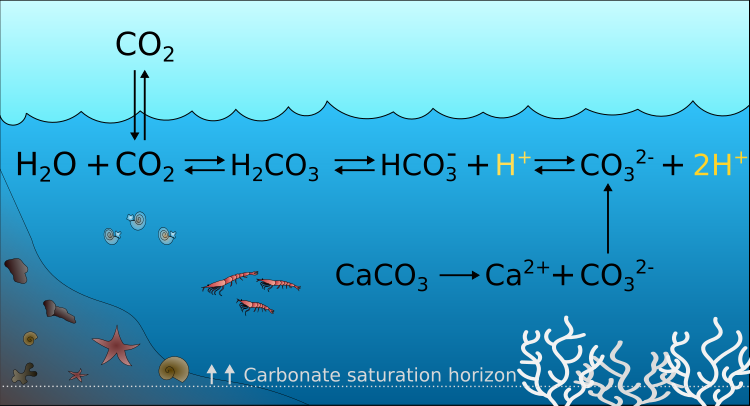
The ocean is one of the largest sinks of atmospheric CO₂, absorbing about 25% of anthropogenic carbon emissions. This uptake of carbon through the ocean-atmosphere interface impacts the chemical balance of the surface waters. CO₂ enters the ocean, dissolves and reacts with water, leading to higher hydrogen ion levels and making the water more acidic.
Ocean acidification (OA) not only causes a decrease in pH but also affects the saturation states of calcium carbonate minerals, particularly aragonite, by lowering the abundance of carbonate ions.
For more information on editing stories, see this blog post.